Let's get to know Bri Milden, Help Desk Technician/NOC Technician at Intrada Technologies and a talented member of our team who brings dedication, expertise, and enthusiasm to her role every day.Intrada: Can you tell us a little about your professional background and what led you to our company?Bri:...
What is Zero Trust Security?
Information Technologies | David Steele | Thursday, February 20, 2025Overview
Zero Trust Security is a modern cybersecurity approach that assumes no user or device should automatically be trusted, requiring constant verification and strict access controls to minimize risks. Unlike traditional models, which rely on perimeter defenses, Zero Trust focuses on proactive prevention, adaptability, and minimizing the impact of potential breaches.

Cybersecurity threats are evolving at an alarming rate, leaving organizations of all sizes vulnerable to breaches that could compromise sensitive data, disrupt operations, or cause financial devastation. But as the threat landscape grows more complex, so too must the approach to security. Enter Zero Trust Security, a paradigm shift in cybersecurity that focuses on proactive prevention rather than reactive defense.
In this post, we’ll explore the concept of Zero Trust Security, how it compares to traditional security, and why it’s becoming the go-to model for businesses aiming to protect their assets. We’ll also discuss actionable strategies for implementing Zero Trust principles, aligning them with operational needs, budgets, and even cyber insurance considerations. By the end of this article, you’ll understand how Zero Trust can play a pivotal role in safeguarding your business.
A New Approach to Cybersecurity
What Is Zero Trust Security?
At its core, Zero Trust Security is a strategic approach that assumes no user, device, or system is inherently trustworthy—even if they’re inside the organization’s network perimeter. Unlike traditional security models, which often rely on perimeter defenses (like firewalls) to block external threats, Zero Trust operates by continually verifying and limiting access to ensure that both external and internal threats are minimized.
This proactive model is built around three key principles:
- Never trust, always verify: All users and devices must be authenticated and authorized before accessing resources.
- Limit access by context: Access is only granted to specific resources under specific circumstances, and it’s revoked automatically when no longer necessary.
- Assume breach: Organizations work under the assumption that breaches will happen, focusing on minimizing damage and recovering quickly.
Traditional Security vs. Zero Trust Security
To better understand Zero Trust, it’s helpful to compare it with traditional, reactive cybersecurity approaches.
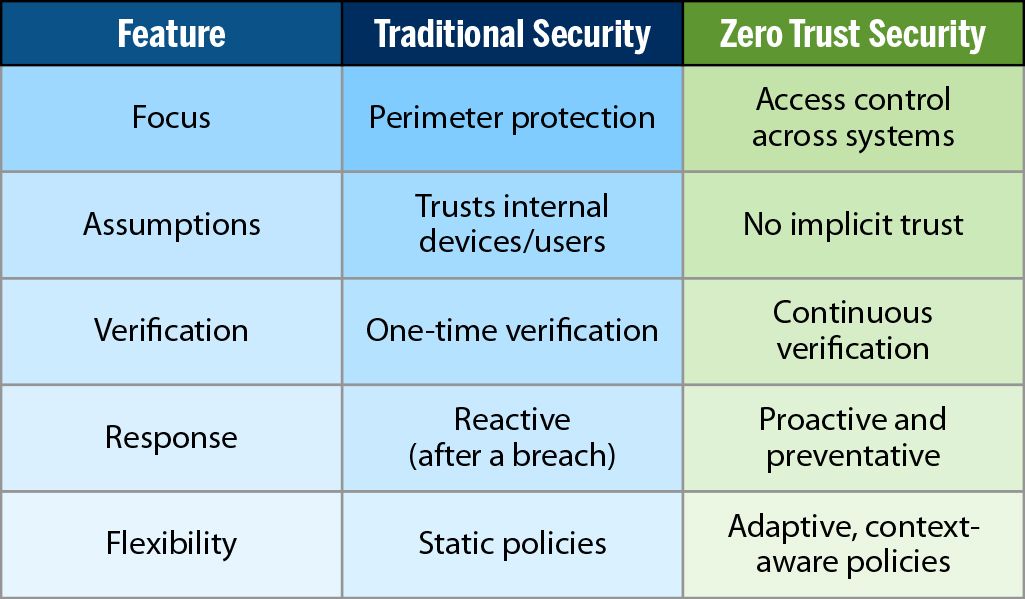
Traditional security models provide a one-size-fits-all solution, which often leaves businesses vulnerable to more sophisticated attacks. Zero Trust, by contrast, is dynamic and adaptable, delivering stronger safeguards against emerging threats.
Why Businesses Should Look Beyond Marketing Hype
The term "Zero Trust" is often surrounded by bold claims and marketing buzzwords aimed at selling the latest cybersecurity tools. While technology plays a critical role in any security setup, it’s important for businesses to approach Zero Trust with a balanced perspective.
Here’s what to keep in mind:
- Conduct a Security Audit First: Before making any investments, audit your existing systems to identify key vulnerabilities and gaps. This allows you to prioritize improvements based on risk level.
- Align Security Needs with Risk Tolerance: Not every company needs the most advanced (and expensive) tools. Consider your risk tolerance—are you protecting highly sensitive customer data, or is your key priority shielding operational systems? Knowing the level of impact a cyber incident could have on your business helps you determine the level of protection required.
- Budget Alignment Matters: Technology solutions can quickly become expensive. Assess your cybersecurity needs, risk tolerance, and available budget to create a strategy that delivers the right level of protection without overspending.
At Intrada, we believe that technology alone is never the solution. Instead, success comes from selecting the right tools, thoughtfully configuring them, and continually monitoring their performance. With careful planning and alignment, a Zero Trust framework can be both effective and cost-efficient.
How Cyber Insurance Fits Into the Picture
Cyber insurance offers financial backup in the event of a breach, but it’s not a substitute for robust security measures. Having the right configurations and controls in place can directly affect your policy terms, coverage eligibility, and premiums. Here’s how Zero Trust impacts your cyber insurance:
- Better Premium Rates: Insurers may reward businesses with reduced premiums if they demonstrate strong security protocols like
Multi-Factor Authentication MFA - Stronger Claim Validity: Some insurance providers require proof of specific measures to process breach claims. Configurations compliant with Zero Trust principles often fulfill these requirements.
Remember, cyber insurance is a complement to—not a replacement for—a strong security framework. The best approach is to assume responsibility for your cybersecurity while using insurance as added protection for worst-case scenarios.
Steps to Implement Zero Trust Security

Transitioning to a Zero Trust model doesn’t happen overnight, and it requires a carefully planned process tailored to your business needs. Here’s a simple roadmap to get started:
- Start with a Comprehensive Audit
Map out your current IT infrastructure, identifying critical assets, entry points, and existing vulnerabilities. This will help prioritize which systems need immediate attention. - Define Access and Authentication Rules
Establish strict access controls tailored for different users and devices. ImplementMFA - Adopt the Principle of Least Privilege
Limit user access to only the systems or data necessary to perform their roles. By restricting privileges, you reduce the potential damage of insider threats or compromised accounts. - Monitor and Analyze Network Activity
Deploy tools for real-time monitoring and anomaly detection. Zero Trust policies are dynamic, so regular reviews and updates are essential to stay ahead of new threats. - Choose and Configure Your Tools Wisely
Select cybersecurity tools that align with your needs and budget. Whether it’s firewalls, endpoint security, or cloud-based solutions, ensure they integrate seamlessly with your operations. - Train Employees
The human factor is one of the most significant vulnerabilities in any security setup. Provide regular training on best practices, phishing awareness, and the importance of data protection. - Review and Refine Over Time
Zero Trust is a continuous process. Regular updates, quarterly audits, and staying informed about the latest threats will keep your business secure.
Build Security Without Compromising Your Budget
At Intrada, we pride ourselves on taking a service-first approach to security. We don’t push expensive tools or scare tactics. Instead, we focus on aligning your organization’s unique risks and goals with the correct configurations and processes to achieve Zero Trust. Our priority is to empower your business with the knowledge and solutions to succeed—not just survive.
Take the First Step Toward Better Security
Your organization’s security needs are important, and we’re here to help. Schedule time with one of our experienced IT Security Professionals to discuss your concerns, explore a network security audit, or learn more about achieving Zero Trust. Together, we’ll identify the solutions that work best for your business without overstretching your budget.

Cybersecurity Awareness Poster
The Evolution of Wireless Networks and Why Bu...
Wireless networks are the backbone of modern business operations. From facilitating seamless remote work to supporting real-time communication across teams, wireless connectivity plays a central role in how businesses operate today. However, as useful as wireless technology is, the rapid pace of its...
Contact Us
- 800-858-5745
31 Ashler Manor Drive
Muncy, PA 17756
Office Hours
Monday - Friday
8 AM - 5 PM EST
Intrada Technologies


Copyright © 2025 - Intrada Technologies - Privacy Policy and Disclaimer
Our website uses cookies and analytics to enhance our clients browsing experience. Learn More /

